Studying Gaussian Processes for Propagating Uncertainty
February 20, 2021
Keywords: machine learning, control theory
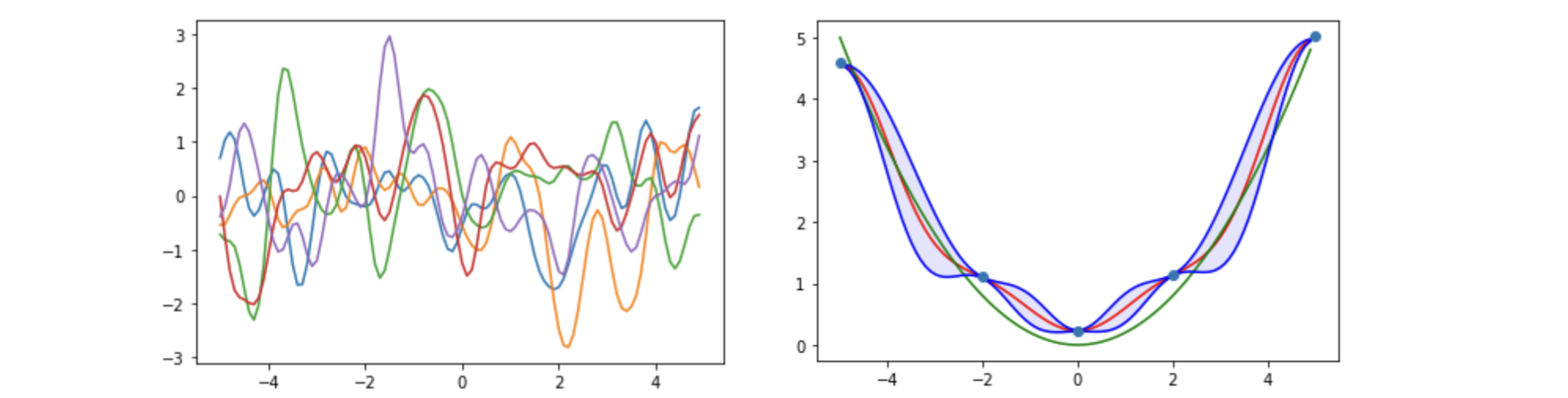
Gaussian Processes (GPs) are a powerful data-driven tool for approximating unknown or expensive to evaluate functions. GPs are specifically useful for time-series prediction which is for example used in Control to model dynamical systems. GPs ability to express the uncertainty of the relative prediction renders them especially useful here.
GPs come with the downside that their computational effort does not scale well with large amounts of data. They are additionally difficult to evaluate at random inputs as there is no closed-form solution for such evaluations. Unfortunately the conventional ways of approximating the propagation of uncertainty underestimate it. Both of these drawbacks are reducing the applicability of GPs in Control. I am addressing these issues in the report by summarizing a range of recent state-of-the-art solutions to these challenges.
